Calculate Receivable Aging
June 27, 2022 - by Bill Jelen

Problem: I have a worksheet showing open invoices. I want to calculate how many days old each unpaid invoice is.
Strategy: Subtract the invoice date from the TODAY() function. The TODAY() function will give you the current date. Each day that you open the workbook, the calculation will update.
Gotcha: You want the number of days. Excel will guess that you want the answer as a date. After entering the formula, change the number format back to numeric.
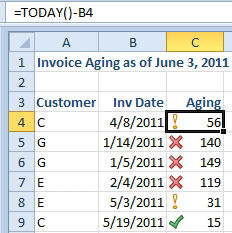
Additional Details: The title in cell A1 is created using TODAY as well. The formula is =”Invoice Aging as of “&TEXT(TODAY(),”MMMM d, YYYY”).
Additional Details: The icons in column C were added using Conditional Formatting. You will read about icon sets in Part IV of this book. The accountant in me could not resist analyzing the result, even though this data is completely fictitious!
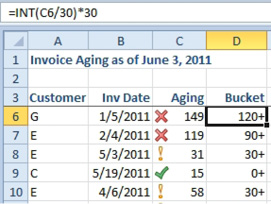
You might want to categorize the receivables into 30-day buckets. The formula in D4 will show 30 for any invoices that are between 30 and 59 days old. The formula is =INT(C6/30)*30. Say that you divided column C by 30 and then took the INT of the result. Everything from 0 to 29 would be classified into Bucket 0. Everything from 30 to 59 would be classified as Bucket 1. I multiply that bucket number by 30 to provide a better name for each bucket. To get the plus sign to show, use a custom number format of 0+.
This article is an excerpt from Power Excel With MrExcel
Title photo by Steve Johnson on Unsplash
